Maintenance of reel primary and secondary reeling devices
Jan 23, 2018
The maintenance schedules for a typical reel are presented in this article. Figures 1 and 2 provide an overview of the main components in a reel. An example reel with a horizontally mounted drive motor is shown in Figure 1. Figure 2 shows an example reel's secondary arms and rails, with the primary arms removed for clarity.
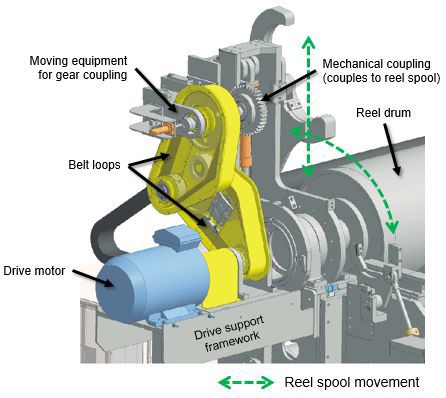
Figure 1 Typical primary drive (horizontally mounted motor)
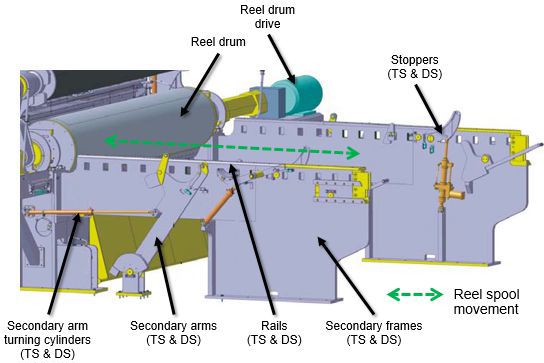
Figure 2 Typical secondary arms and rails
The following maintenance instructions are for an example reel.
The example primary reeling device (Figures 3 and 4) includes a vertically mounted drive, turnbuckle/cylinder/cross shaft system to move and maintain alignment of the primary arms, linear guideways and cylinders for the primary carriages un/loading movement, primary clamp arms/cylinders to clamp the reel spool, drive belts and guards to transmit rotational force from the drive motor to the reel spool and all necessary sensors.
The example secondary reeling device (Figure 5) includes secondary arms, movement cylinders and necessary sensors.
NOTE: Do not put a magnet in the immediate vicinity of the position sensors. The magnet will interfere with the operation of the sensor.
NOTE: For coupling and gearbox, refer to original manufacturer's instructions.
Primary reeling device maintenance
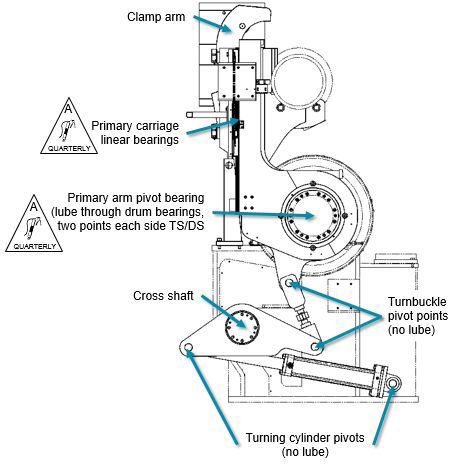
Figure 3a Primary reeling device - bearings, clamp & turnbuckle
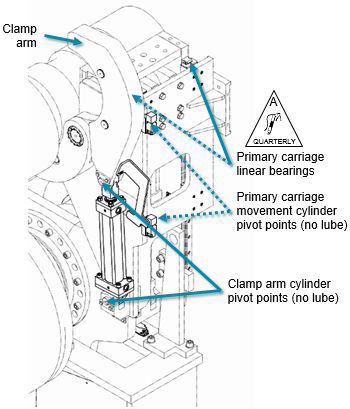
Figure 3b Primary reeling device - clamp arm, clamp and carriage cylinders
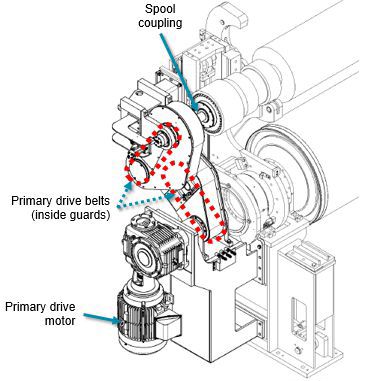
Figure 3c Primary reeling device - belts and vertically mounted motor
Daily maintenance
Check operation and sound of the drive motor.
Check operation of spool guide assembly. Notify maintenance if shock absorber is not operating properly so it can be replaced.
The belt guards of the drives must be unbroken. Make sure that the exterior of the primary center drive is clean. Clean the motor fan if necessary.
Monthly maintenance
Inspect hydraulic cylinders for operation and leaks while the machine is running. Repair kits are available.
Check operation of limit switches.
Check the condition and operation of the linear guideways. No scratches, dents or signs of corrosion are allowed on the guideways. Check the amount of lubricant and the seal condition. A surface trace wiped by the seal must be visible in the protective grease of the guideway.
Quarterly maintenance
Lubricate the relieving/loading carriage linear bearings.
Lubricate primary arm pivot bearings.
Check the primary drive timing belts of the drives for wear. The condition of the belt teeth can be checked visually by opening the cover.
Check the tension of the primary drive cogged belt. Too loose a belt skips over the teeth. Find out what is causing the problem and if necessary, replace the belt. Cogged belt tension should be included in the mechanical drawings. See the component brochures for component specific instructions.
Check noise, temperature, vibration and oil level of gearbox.
Check condition of loading rollers and clamping wear blocks. Replace as necessary.
Check and lubricate the slide bearing for primary reeling device turning.
Lubricate primary drive splined output shaft with standard EP2 lubricant, grease gun.
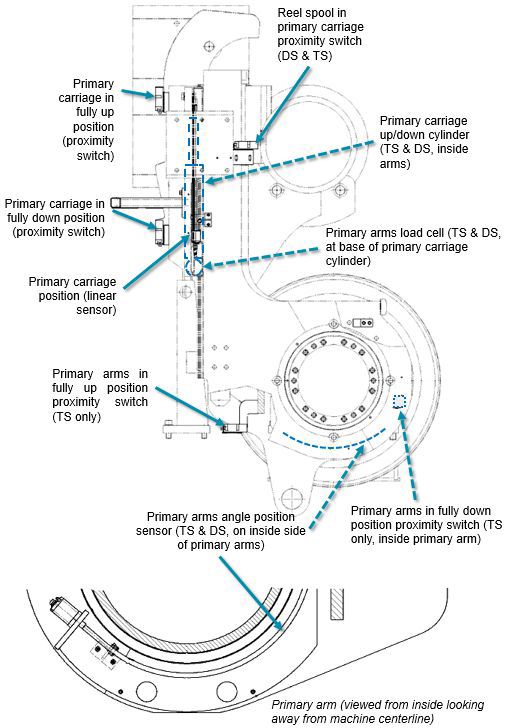
Figure 4a Primary reeling device sensors
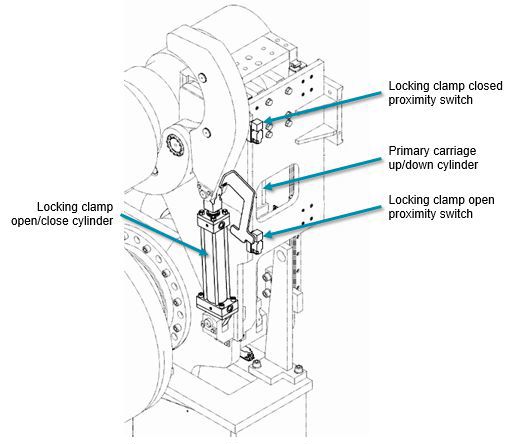
Figure 4b Primary reeling device sensors, locking clamp
Semi-annual maintenance
Check the load cells for drift of the zero values, TS and DS. The zero point is set only if the value has drifted. The limit value is 0.5 kN. The setting can be made during a web break or shutdown. Reset the sensor on the maintenance display.
Check cleanliness and operation of the carriage position sensors and proximity switches. If necessary, clean them when the machine is shut down.
Check operation of the primary arms position sensors and proximity switches.
Check the hydraulic pressures of the turning cylinders during turning. The pressures are measured on both sides of the cylinder piston. The pressure difference must not exceed 20 bar (290 PSI). A big pressure difference may result from a failure in cylinder seals or in the counter-balance valve, or it may result from an improper adjustment of the counter-balance valve. The components are replaced or adjusted. The adjustor screws of both counter-balance valves must be open by three rotations.
Annual maintenance
Check the alignment of the primary arms.
Check the condition of the clamping arm pivot bushings; replace as necessary.
Check the condition of clamping arm pivot pins; lubricate as necessary.
Check the condition of the primary arm pivot bushings. Replace as necessary.
Check the condition of the synchronizing shaft bearings.
Maintain the linear guideways). Wipe clean with white spirit. Protect with CONTRAKOR A 40 F Spray or similar. The protective coating must be visible.
Lubricate lower shaft floating bearing, standard lithium, hand pack.
Lubricate lower shaft held bearing, standard lithium, grease gun.
Lubricate slewing bearing, standard EP2, grease gun. Grease all four (4) fittings because of small rotation angle.
Lubricate intermediate shaft held bearing, standard lithium, grease gun.
Lubricate intermediate shaft floating bearing, standard lithium, hand pack.
Other
Every 2 years, replace the primary drive timing belts.
Every 3 years, maintain the gear coupling of the primary drive moving mechanism slide. Wash and relubricate the coupling. Check the condition of the cogs. Any impending damage caused by misalignment or overloading can now be detected and repaired in time.
Every 3 years, maintain all hydraulic cylinders TS and DS. Replace the seals and spherical bearings. Replace the turnbuckle bearings when maintaining the turning cylinders.
Every 5 years, remove the primary arms and check the condition of the pivot bearing housings.
Secondary arms maintenance
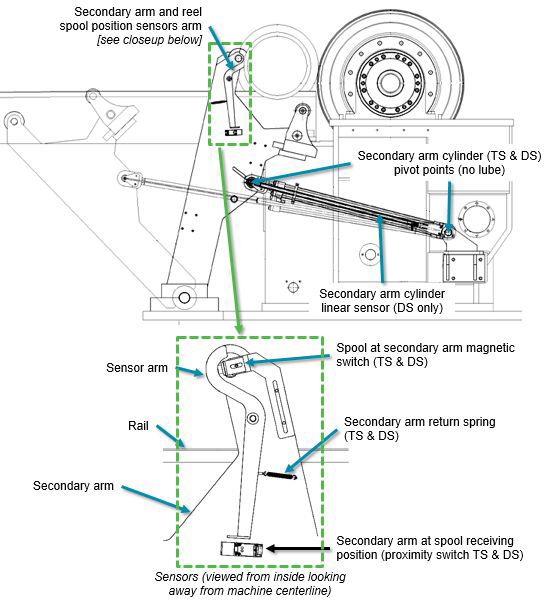
Figure 5 Secondary arm assembly and sensors
Daily maintenance
Check operation of hydraulic cylinders while machine is running.
Monthly maintenance
Check for leaks of hydraulic cylinders while machine is running. Repair kits are available. See supplier datasheets for repair instructions.
Quarterly maintenance
Check condition of cylinder rod end and clevis bearings.
Semi-annual maintenance
Check cleanliness and operation of the position sensors and proximity switches. If necessary, clean them when the machine is shut down.
Annual maintenance
Check torque of loading/ejecting cylinder mounting bracket screws.
Other
Every 3 years, maintain hydraulic cylinders TS and DS. Replace the seals and spherical bearings.
For assistance with reel maintenance, contact your Valmet representative.